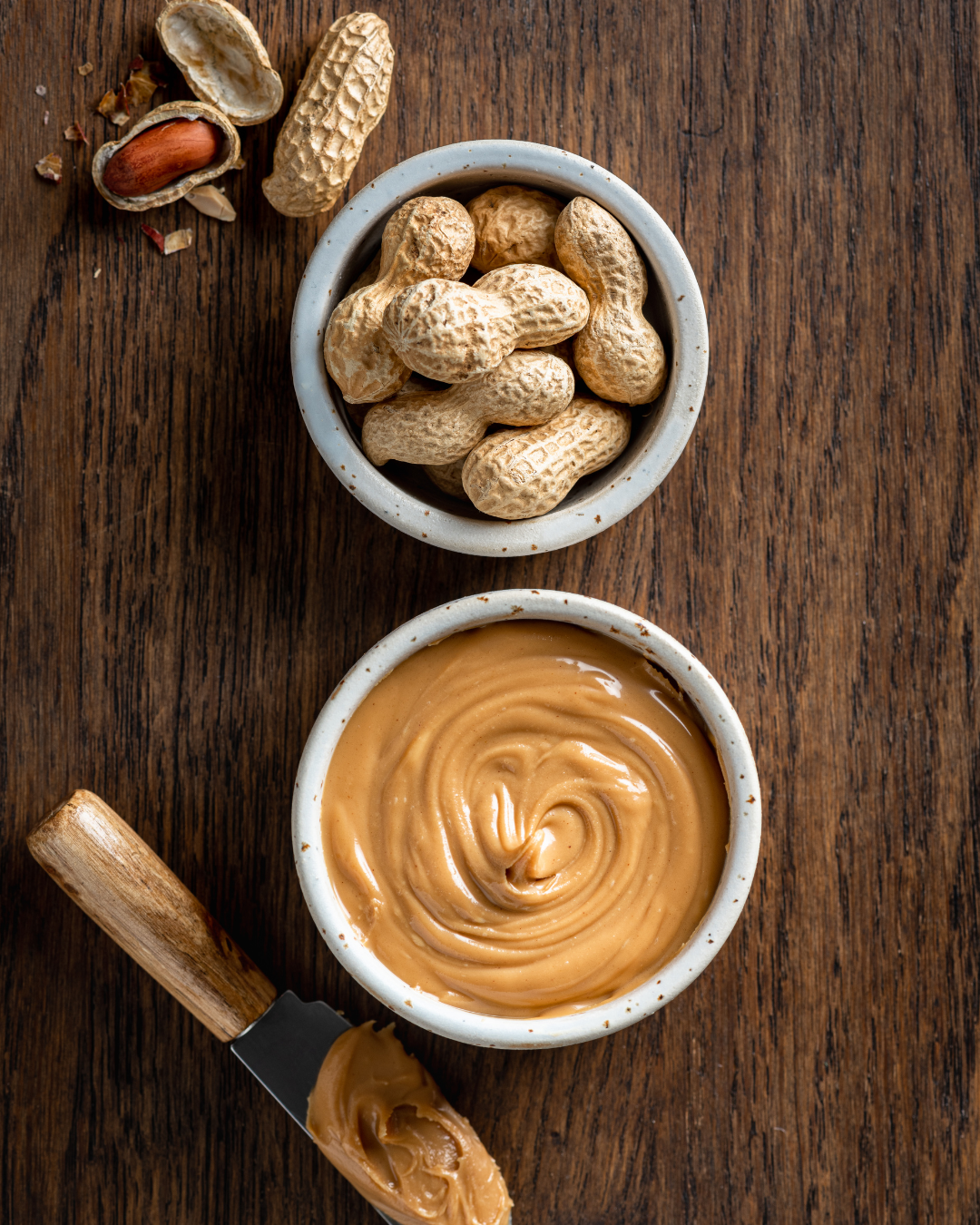
Peanut butter has long been a beloved pantry staple for many, providing a tasty and versatile addition to meals and snacks. However, when it comes to pursuing fitness goals, whether it’s weight loss, muscle gain, or general health improvement, it’s crucial to make informed dietary choices.
One of the primary reasons why peanut butter might hinder your fitness goals is its high calorie density. While it can be an excellent source of healthy fats and protein, it’s also incredibly calorie-dense.
Just two tablespoons of peanut butter can contain around 200 calories. When aiming for weight loss or a calorie deficit, the calories in peanut butter can add up quickly and potentially hinder your progress.
Portion control is crucial when it comes to achieving fitness goals. Unfortunately, peanut butter can be challenging to measure accurately due to its sticky nature.
It’s easy to exceed the recommended portion size, leading to unintended calorie surplus and hindered progress. Overconsumption of peanut butter can derail weight loss efforts and even result in weight gain.
While peanut butter is often touted for its healthy fats, it’s important to remember that fat contains more than double the calories per gram compared to protein or carbohydrates.
Although these fats can be beneficial in moderation, consuming excessive amounts of peanut butter can easily lead to consuming excess calories, which can hinder your fitness goals.
Peanut allergies are relatively common, affecting approximately 1-2% of the population. For individuals with peanut allergies, consuming peanut butter can lead to severe allergic reactions. If you have a known peanut allergy, it’s essential to avoid peanut butter entirely to prioritize your health and well-being.
While peanut butter does contain healthy fats, it is worth noting that it is particularly high in omega-6 fatty acids. While omega-6 fatty acids are essential for the body, an imbalance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids can contribute to inflammation.
Many Western diets are already abundant in omega-6 fatty acids, and excessive consumption of peanut butter may exacerbate this imbalance.
Commercial peanut butter often contains additional ingredients, such as hydrogenated oils, added sugars, and salt, which may compromise its nutritional value.
These additives can increase the calorie content and contribute to health issues such as weight gain and high blood pressure. Moreover, some peanut butter brands may process their products in facilities that handle other allergens, increasing the risk of cross-contamination for individuals with allergies.
For some individuals, peanuts and peanut butter can pose challenges to digestive health. They contain phytic acid and enzyme inhibitors, which can impair the absorption of minerals and enzymes in the body. Additionally, the high fat and fiber content in peanut butter can lead to digestive discomfort, especially for those with sensitive digestive systems.
While peanut butter can be a delicious and nutritious food for some, it may not be suitable for everyone, particularly for those with specific fitness goals. When it comes to pursuing weight loss, muscle gain, or overall health improvement, it’s essential to evaluate your dietary choices carefully.